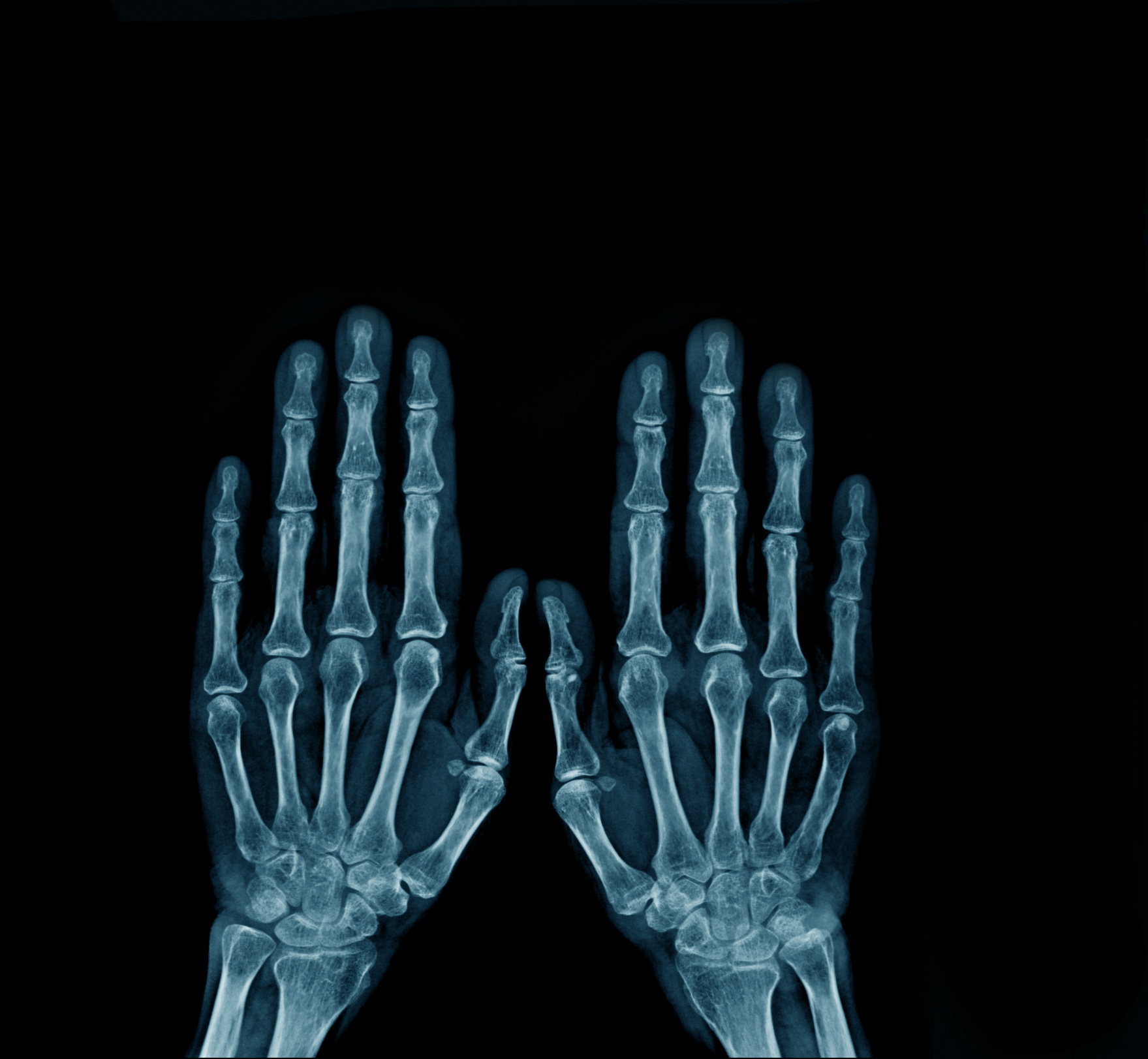
According to a press release from the ACR, a novel deep-learning model may accurately identify and predict joint damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. In a new study—presented by Hitchon et al at ACR Convergence 2023—researchers used version 516 of the convolutional neural network–based You Only Look Once algorithm to develop a deep-learning model designed to automate the detection of joint space narrowing and erosions in the hand radiographs of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The researchers trained the model with 240 training and 89 evaluation pediatric hand radiographs and validated it with 54 clinician-labeled radiographs from four adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis. They then applied a vision transformer model to predict joint space narrowing and erosions, which worked by splitting the images into small patches, transforming or flattening them into sequences, creating low-dimensional linear embeddings, adding positional embeddings, and feeding the encoded sequences into standard transformer encoders. This process was further validated with over 2,200 radiographs from 381 patients. The deep-learning model accurately identified target joints and demonstrated highly accurate predictions for joint space narrowing and erosions. Despite the positive results, the study authors concluded: “[Artificial intelligence] models cannot replace human radiologists at this stage, but they will be excellent complementary tools that can enhance the overall quality and efficiency of radiograph scoring analysis when used in conjunction with radiologist judgment.”