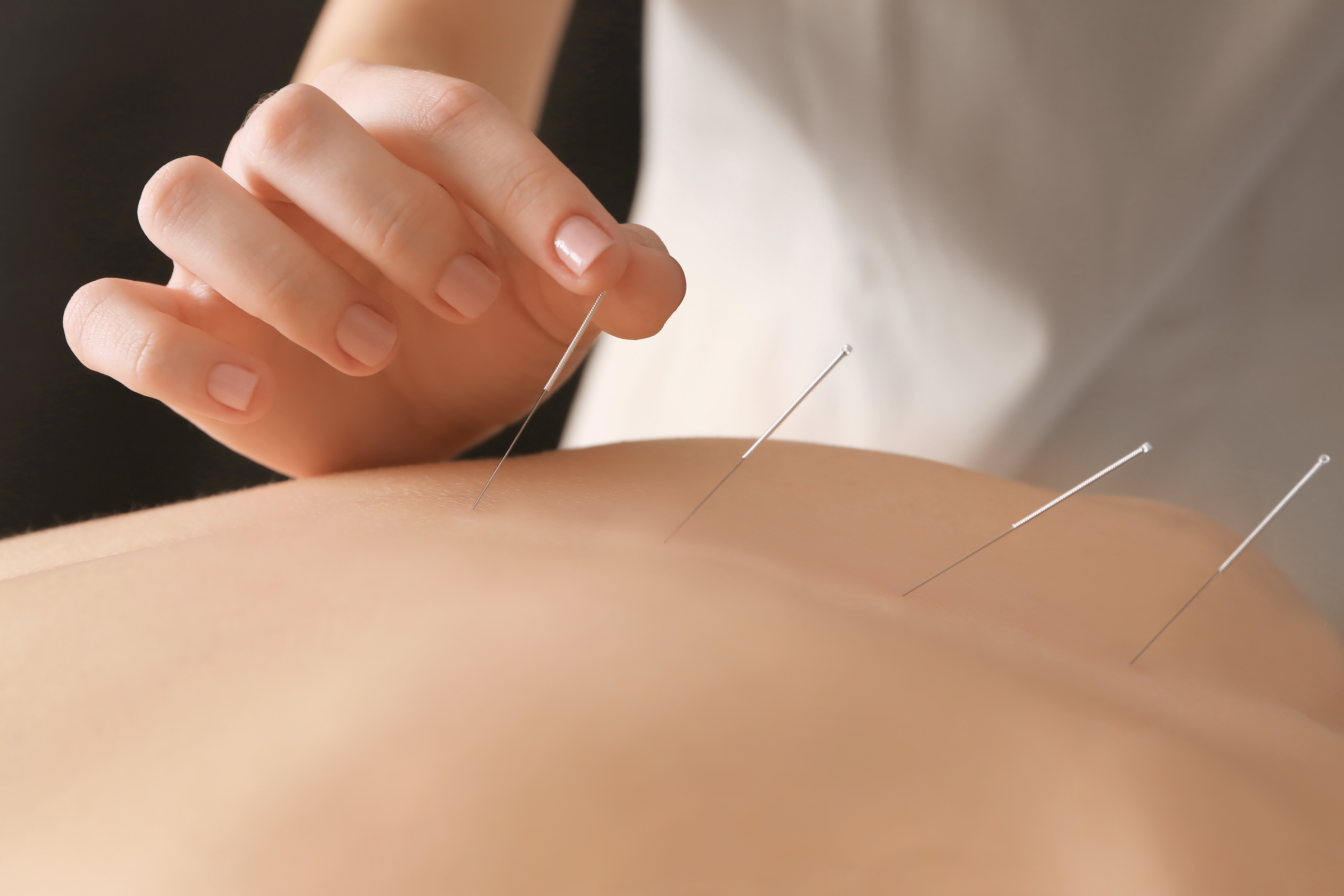
Acupuncture may reduce the risk of ischemic stroke in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, according to a recent study published by Huang et al in BMJ Open. In the study, investigators used the National Health Insurance Research Database in Taiwan to analyze the outcomes of 23,226 patients with newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis who either underwent or did not undergo acupuncture therapy between 1997 and 2010. Compared with those in the no-acupuncture group, patients in the acupuncture group had a lower cumulative incidence of ischemic stroke. Three hundred and forty-one (5.95 per 1,000 person-years) of the patients who underwent acupuncture vs 605 (12.4 per 1,000 person-years) of the patients who did not undergo acupuncture experienced ischemic stroke (adjusted subhazard ratio = 0.57, 95% confidence interval = 0.50–0.65). The investigators underscored that acupuncture may benefit patients with rheumatoid arthritis. In a companion press release from the BMJ, the study authors concluded: “Unstable blood pressure and lipid profiles are the two risk factors for ischemic stroke, and acupuncture therapy has the advantage of controlling both hypertension and dyslipidemia.”